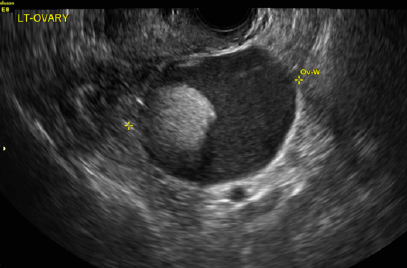
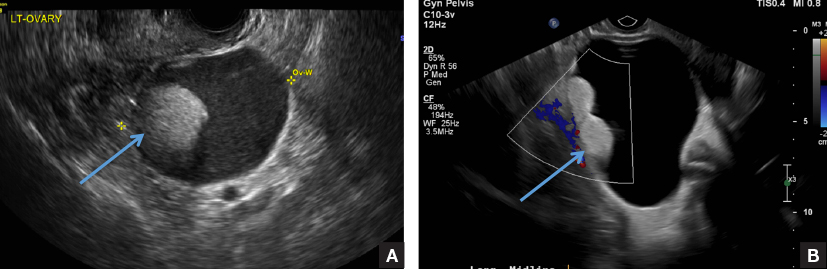
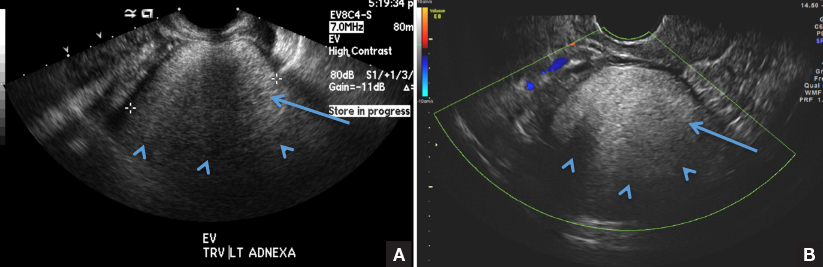
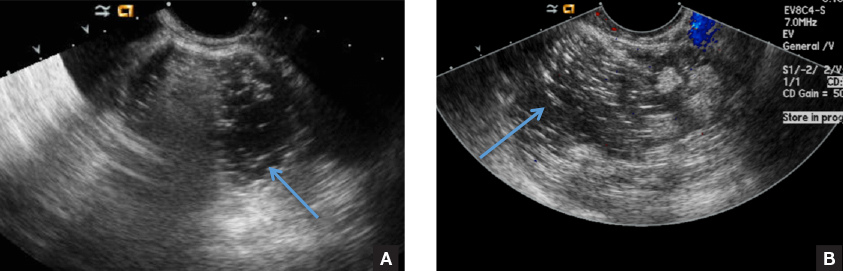
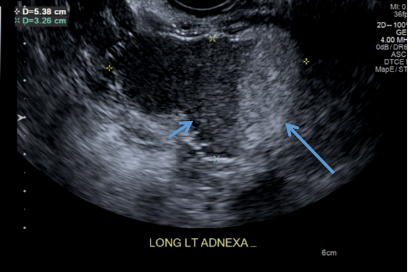
A) Dermoid plug CORRECT
The most common appearance of an ovarian dermoid is a cystic lesion with a focal echogenic nodule protruding into the cyst (Rokitansky nodule).1
B) Tip-of-the-iceberg sign INCORRECT
The next most common appearance of an ovarian dermoid is a focal or diffuse hyperechoic mass with areas of sound attenuation from the sebaceous material and hair, often called the tip-of-the-iceberg sign.1
C) Dot-dash pattern INCORRECT
The 3rd most common appearance of an ovarian dermoid is a cystic lesion with multiple thin echogenic bands (lines and dots) that visualize hair floating within the cyst.1
D) Fat-fluid level INCORRECT
The 4th most common appearance of an ovarian dermoid is a result of the echogenic sebum and hypoechoic serous fluid causing a fat-fluid level.1